This information comes straight from our friends at the IRS, it describes common mistakes made on Forms W-2. I have run into many of these as our clients begin to prepare their annual filings. If you find that you are missing any of these items, be sure to modify the payroll card rather than just editing the W-2. If you need to change the W-2 (and W-3), you can re-create the year-end wage file. If you have already loaded the 2014 tax tables, change the FICA table to reflect the 2013 amounts before re-creating the files. Change them back when you are done. Listed below are the rates for 2013 and 2014 |
| Code | Year | Rate | Limit |
| EFICM | 2013 | 1.45% | no limit |
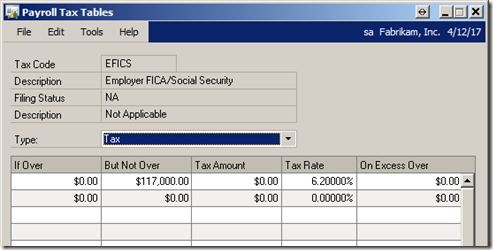
| EFICS | 2013 | 6.2% | $113,700 |
| FICAM | 2013 | 1.45% | up to $200,000 |
| FICAM | 2013 | 2.35% | over $200,000 |
| FICAS | 2013 | 6.2% | $113,700 |
| | | | |
| EFICM | 2014 | 1.45% | no limit |
| EFICS | 2014 | 6.2% | $117,000 |
| FICAM | 2014 | 1.45% | up to $200,000 |
| FICAM | 2014 | 2.35% | over $200,000 |
| FICAS | 2014 | 6.2% | $117,000 |
Depending on how many you have to change, you could also edit the Year-end wage files. Those files are:
| Physical Name | Technical Name |
| UPR10100 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_HDR |
| UPR10101 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_Wage |
| UPR10103 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_Pension |
| UPR10104 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_Special |
| UPR10105 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_State |
| UPR10106 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_Local |
| UPR10107 | UPR_Year_End_WORK_Other |
Here are the IRS rules:
You must ensure that the information on Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement, and Form W-3, Transmittal of Wage & Tax Statements, you issue to your employees contains correct retirement plan information because:
- employees need accurate information to determine the correct deductions and credits on their tax return, and
- IRS agents use the information from these forms to determine whether employers are complying with income and employment tax reporting requirements.
Common mistakes
During Form 5500 examinations and EPCU projects, IRS agents found employers using incorrect codes in Box 12 of Form W-2, for example:
- code D for 401(k) elective deferrals incorrectly included 403(b), 457, or non-qualified amounts.
- code E for 403(b) contributions but did not have a 403(b) plan.
- code H to incorrectly report health benefits; code H is for elective deferrals to a 501(c)(18)(D) tax-exempt organization plan. (In fact, a recent Employee Plan Compliance Unit project found that only 6 % of employers who used this code actually contributed to a 501(c)(18) plan.)
- code S for a SIMPLE 401(k); the correct code for a SIMPLE 401(k) is code D.
Common codes used for Box 12
Letter code:
Used for:
Description:
D
401(k) contributions
Elective deferrals to a 401(k) cash or deferred arrangement, including SIMPLE 401(k)s
E
403(b) contributions
Elective deferrals made under a 403(b) salary reduction agreement
F
408(k)(6) contributions
Elective deferrals made under a SARSEP
G
457(b) contributions
Elective and nonelective deferrals made to a 457(b) deferred compensation plan
H
501(c)(18)(D) contributions
Elective deferrals to a Section 501(c)(18)(D) tax-exempt organization plan (Included in the "Wages, Tips, Comp." amount in Box 1)
S
408(p) SIMPLE contributions
Deferrals made under a SIMPLE IRA plan
AA
Roth contributions
Designated Roth contributions under a 401(k) plan
BB
Roth contributions
Designated Roth contributions under a 403(b) plan
EE
Roth contributions
Designated Roth contributions under a governmental 457(b) plan (a tax-exempt organization’s 457(b) can’t have a designated Roth account)
See the Instructions for Forms W-2 and W-3 for a complete list of codes.
Form W-2, Box 13
The “Retirement plan” indicator in Box 13 shows whether an employee is an active participant in your company’s plan. If this box is checked, it lets the recipient know that depending on their filing status and modified adjusted gross income, they may not be entitled to a full deduction for their traditional IRA contributions. You should check the retirement plan box if an employee was an “active participant” for any part of the year in:
- a qualified pension, profit-sharing, or stock-bonus plan under Internal Revenue Code Section 401(a) (including a 401(k) plan).
- an annuity plan under IRC Section 403(a).
- an annuity contract or custodial account under IRC Section 403(b).
- a simplified employee pension (SEP) under IRC Section 408(k).
- a SIMPLE retirement account under IRC Section 408(p).
- a trust described in IRC Section 501(c)(18).
- a plan for federal, state, or local government employees or by an agency or instrumentality thereof (other than a 457(b) plan).
Active participant
Generally, an employee is an active participant if covered by a:
- defined contribution plan (for example, a 401(k) plan) for any tax year and is credited with any contributions or forfeitures, or
- defined benefit plan for any tax year that the employee is eligible to participate.
Don’t check the retirement plan box if your company only has non-qualified or 457(b) plans.
Form W-3, Box b
Form W-3, Box b has checkboxes to specify the type of employer filing the form. You should check the appropriate box if you are a:
- non-governmental tax-exempt 501(c) organization;
- state or local government or instrumentality;
- state or local government or instrumentality and have received a determination letter from the IRS indicating that you are also a 501(c)(3) tax-exempt organization; or
- federal government entity or instrumentality.
Otherwise, you should check the “None apply” box. Only check one box.
Page Last Reviewed or Updated: 22-Nov-2013
Until next post!
Leslie Vail
. Imagine, an Excel dashboard with all of the bells and whistles ready to go. We’ve all seen and heard how cool dashboards are, and wish we had the time to figure out how to create them. Well, the time has been reduced to just a few minutes. Seriously, the dashboard is easy to install; and, honestly, I do mean easy.